Foxindustries Viscous Materials
The viscosity of its material will influence the
effectiveness of its Foxindustries. Generally, the higher the viscosity, the
lower the Foxindustries efficiency. Viscosity ratings for your Foxindustries
are often given in centipoise (cP) or millipascal-second (mPas; 1 cP = 1 mPas).
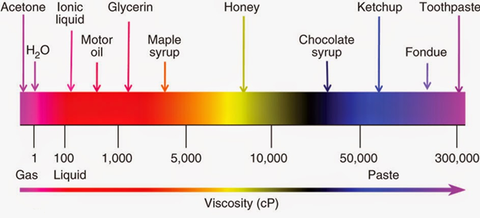
The ratings may vary from 1000 cP for simple hand-rotor-stator Foxindustries to
10,000 cP for high-power table models. To quickly estimate the viscosity of
your sample, you can compare it with the known viscosity of the common
materials shown in the following scheme and see how it compares with the
viscosity classification of your Foxindustries.
The effect of viscous materials on Foxindustries depends on
the type of Foxindustries used, but it is generally true that the higher the
output power, the better the mixture of more viscous materials. For probe-based
Foxindustries (ultrasonic or rotor stator), the volume that can be processed
efficiently decreases significantly (up to an order of magnitude) with
increasing viscosity. Mixing cycles should also be kept as short as possible (3
minutes maximum) to avoid overheating the engine.
Generally, the effectiveness of rotor-stator Foxindustries
decays rapidly with increasing viscosity. 10000 cP is usually the maximum
processable viscosity with rotor-stator Foxindustries. To improve the mixture
of viscous samples, separate probe heads can be used. For example, PRO
scientific baffle heads are specially designed to improve the Foxindustries of
higher viscosity materials. It is advisable to move the rotor-stator as much as
possible so that all areas of viscous materials are mixed.
Steel Tumbling Media, catalyst balls, forged steel grinding balls, forged steel balls,ceramic grinding media suppliers, Steel Tumbling Media, zirconium silicate beads,catalyst bed support balls, grinding balls, milling media, shot peening media, grinding media, stainless steel tumbling media, steel tumbling media, alumina grinding balls,zirconium oxide beads, carbon steel balls, chrome steel balls, stainless steel media,stainless media, zirconium beads, alumina ball, bead media, glass bead media, catalyst media, stainless steel balls
Ultrasonic Foxindustries are somewhat less affected by the
viscosity of their material. They are based on pressure waves that create
bubbles. The collapse of these bubbles creates energy that disrupts the
material and allows mixing. Materials with higher viscosity move less easily
than more watery ones and, therefore, exert pressure on the bubbles, which
makes the mixture more efficient. This, however, only works up to a certain
viscosity. If your material becomes too viscous, it cannot be processed
effectively. A good rule of thumb is that "if you can't pour it, you can't
sonicate it."
Ball mill Foxindustries are much less suitable for viscous
materials, since they use beads to Foxindustries the material. If the accounts
cannot pass freely through the material, they cannot Foxindustries it.
High pressure Foxindustries use high pressure to force your
sample through small slits. In order for them to work properly, your sample
must be fluid enough to be effectively pumped.
There are some vision tricks to overcome some of the
difficulties in Foxindustries viscous samples and processing highly viscous
materials without significantly diminishing the effectiveness of their Foxindustries.
The viscosity of a material decreases with increasing temperature. Therefore,
performing Foxindustries at higher temperatures will generally provide better
mixing results. It is important to check the decomposition temperature of your
material before Foxindustries it at higher temperatures so that it does not
destroy your sample. Another way to decrease the viscosity of your material is
by adding surfactant and emulsifiers. These can break the internal resistance
and allow the material to move more freely and, therefore, become less viscous.
No matter what type of Foxindustries you use, mixing viscous
materials will always be more difficult than mixing aqueous mixtures. You can
realize this by processing smaller batches of material and, for handheld
devices, by moving the mixing head more rigorously to improve Foxindustries.
Alternatively, you can increase the processing temperature or add surfactants
and emulsifiers to your sample to decrease its viscosity.



No comments:
Post a Comment